|
Contents
|
Staging of prostate cancer
Τ (Primary tumor)
| Τx | The main tumor cannot be assessed. |
|---|---|
| T0 | There is no indication of existence of tumor |
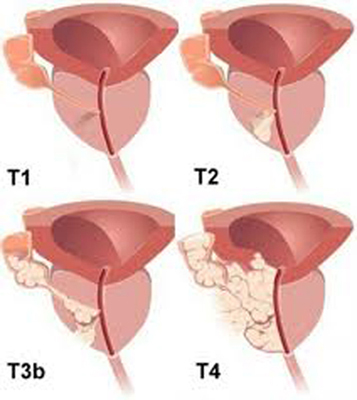
| T1 | Clinically latent tumor, not palpable or visible on the imaging studies |
| T1a | Random histological finding after prostatectomy to 5% or less of the tumor that was removed |
| T1b | Random histological finding after prostatectomy to more than 5% of the tumor that was removed |
| T1c | Diagnosis of the tumor after needle biopsy (e.g. because of increased PSA) |
| T2 | Tumor localized in the prostate gland 1 |
| T2a | The tumor occupies the half or less of one lobe |
| T2b | The tumor occupies more than half of one lobe but not both lobes |
| T2c | The tumor occupies both lobes |
| T3 | The tumor extends beyond the prostatic capsule 2 |
| T3a | Extracapsular expansion (unilateral or bilateral) |
| T3b | The tumor invades the seminal vesicles (either one of them or both) |
| T4 | The tumor is confined or invades other adjacent structures (other than the seminal vesicles) bladder neck, external sphincter, rectum, levator ani muscle or the pelvic floor |
Ν (locoregional lymph-nodes) 3
| Nx | The locoregional lymph nodes can not be assessed. |
|---|---|
| N0 | Absence of no metastasis to the locoregional lymph-nodes. |
| N1 | Metastasis to the locoregional lymph-nodes. |
Μ (metastases)4
| Mx | The distal metastases cannot be assessed. |
|---|---|
| M0 | Absence of distal metastases |
| M1 | Distal metastases |
| M1a | to the non-locoregional lymph-nodes |
| M1b | to the bones |
| M1c | other localizations |
|
Nomograms for prostate cancer
|
Name |
|
|---|---|
|
Special features |
The classic tables that opened the way for the creation and acceptance of nomograms in prostate cancer |
|
What does it calculate? |
Based on PSA, Gleason Score and clinical stage, it calculates the probability of the following: Organ Confined Disease, Extraprostatic Extension, Seminal Vesicle Invasion and Lymph Node Invasion |
|
Creator |
Partin AW |
|
First publication |
Partin AW, Yoo J, Carter HB, Pearson JD, Chan DW, Epstein JI and Walsh PC: The use of prostate specific antigen, clinical stage and Gleason score to predict pathological stage in men with localized prostate cancer. J Urol 150: 110-4, 1993. |
|
References |
746 |
|
Institution / name |
|
|
Link |
|
|
ISUD Evaluation |
*** |
|
Name |
|
|---|---|
|
Special features |
The classic tables that opened the way for the creation and acceptance of nomograms in prostate cancer |
|
What does it calculate? |
Based on PSA, Gleason Score and clinical stage, it calculates the probability of the following: Organ Confined Disease, Extraprostatic Extension, Seminal Vesicle Invasion and Lymph Node Invasion |
|
Creator |
Partin AW |
|
First publication |
Partin AW; Kattan MW; Subong ENP; et al.Title: Combination of prostate-specific antigen, clinical stage, and gleason score to predict pathological stage of localized prostate cancer - A multi-institutional update JAMA 1997; 277(18): 1445-1451 |
|
References |
1087 |
|
Institution / name |
|
|
Link |
|
|
ISUD Evaluation |
*** |
|
Name |
|
|---|---|
|
Special features |
The classic tables that opened the way for the creation and acceptance of nomograms in prostate cancer |
|
What does it calculate? |
Based on PSA, Gleason Score and clinical stage, it calculates the probability of the following: Organ Confined Disease, Extraprostatic Extension, Seminal Vesicle Invasion and Lymph Node Invasion |
|
Creator |
Partin AW |
|
First publication |
Partin AW, Mangold LA, Lamm DM, Walsh PC, Epstein JI and Pearson JD: Contemporary update of prostate cancer staging nomograms (Partin Tables) for the new millennium. Urology. 58: 843-8, 2001 |
|
References |
476 |
|
Institution / name |
|
|
Link |
|
|
ISUD Evaluation |
*** |
|
Name |
|
|---|---|
|
Special features |
The Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial Prostate Cancer Risk Calculator (PCPTRC) was developed on the basis of 5519 men of the placebo group of the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial They all had PSA lower/equal to 3.0 ng/ml and were followed for seven years with PSA and digital prostate examination (DPE) per year. For PSA> 4.0 ng/ml or suspicious DPE, a biopsy was performed |
|
What does it calculate? |
The estimated risk of prostate cancer on biopsy and the risk of having cancer of high-grade of malignancy |
|
Creator |
The Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial Prostate Cancer Risk Calculator (PCPTRC) |
|
First publication |
Thompson IM, Ankerst DP, Chi C, Goodman PJ, Tangen CM, Lucia MS, Feng Z, Parnes HL, Coltman CA Jr. Assessing prostate cancer risk: Results from the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial, Journal of the National Cancer Institute 98: 529-534, 2006. |
|
References |
257 |
|
Institution / name |
|
|
Link |
|
|
ISUD Evaluation |
** |
|
Name |
|
|---|---|
|
Special features |
The tables calculate the result of each patient based on the treatment offered |
|
What does it calculate? |
It calculates the probability of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy at 2, 5, 7 and 10
|
|
Creator |
Kattan |
|
First publication |
Stephenson AJ, Scardino PT, Eastham JA, Bianco FJ Jr, Dotan ZA, DiBlasio CJ, Reuther A, Klein EA, Kattan MW. Postoperative nomogram predicting the 10-year probability of prostate cancer recurrence after radical prostatectomy. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23(28): 7005-12. |
|
References |
157 |
|
Institution / name |
|
|
Link |
|
|
ISUD Evaluation |
*** |
|
Name |
|
|---|---|
|
Special features |
The tables calculate the result of each patient based on the treatment offered |
|
What does it calculate? |
It calculates the probability of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy at 2, 5, 7 and 10
|
|
Creator |
Kattan |
|
First publication |
Kattan MW, Wheeler TM, Scardino PT. Postoperative Nomogram for Disease Recurrence after Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate Cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 1999; 17: 1499-1507 |
|
References |
363 |
|
Institution / name |
|
|
Link |
|
|
ISUD Evaluation |
*** |
|
Name |
|
|---|---|
|
Special features |
The tables calculate the result of each patient based on the treatment offered |
|
What does it calculate? |
It calculates in patients with recurrence radical prostatectomy the probability of successful treatment with salvage radiotherapy (PSA undetectable at 6 years after radiotherapy) |
|
Creator |
Kattan |
|
First publication |
Stephenson AJ, Scardino PT, Kattan MW, Pisansky TM, Slawin KM, Klein EA, Anscher MS, Michalski JM, Sandler HM, Lin DW, Forman JD, Zelefsky MJ, Kestin LL, Roehrborn CG, Catton CN, DeWeese TL, Liauw SL, Valicenti RK, Kuban DA, Pollack A. Predicting the outcome of salvage radiation therapy for recurrent prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. J Clin Oncol. 2007 20; 25(15): 2035-41 |
|
References |
155 |
|
Institution / name |
|
|
Link |
|
|
ISUD Evaluation |
** |
|
Name |
|
|---|---|
|
Special features |
The tables calculate the result of each patient based on the treatment offered |
|
What does it calculate? |
It calculates the probability of survival for one and two years later, in patients with metastatic carcinoma, and progression despite hormone therapy |
|
Creator |
Kattan |
|
First publication |
Smaletz O, Scher HI, Small EJ, Verbel DA, McMillan A, Regan K, Kelly WK, Kattan MW. Nomogram for overall survival of patients with progressive metastatic prostate cancer after castration J Clin Oncol 2002; 20(19): 32-82 |
|
References |
161 |
|
Institution / name |
|
|
Link |
|
|
ISUD Evaluation |
** |